| . |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
To understand the abnormal you have to know the normal. "FAILURE IS NOT AN OPTION" THERE IS MORE STUFF TO BE KNOWN THAN WHAT WE ALREADY KNOW
If you have any question you get my E-mail 1. Human anatomy is the science concern with the structure of the human body. 2. The terms of anatomy are descriptive and are generally of Greek or Latin derivation. 3. The history of human anatomy parallels that of medicine and has also been greatly influenced by various religions.
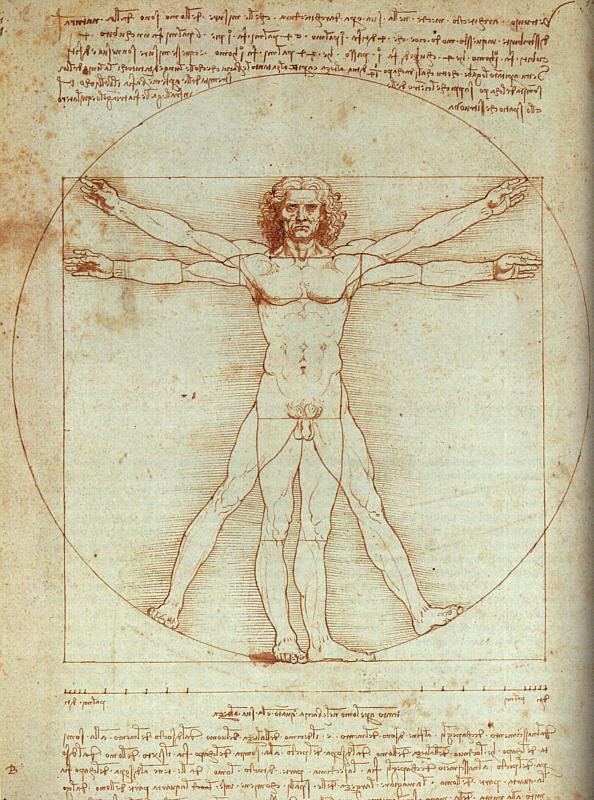
anatomy. (Image by Flickr User Patrick J. Lynch, CC) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
For AP 2 [104] CLICK HERE |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Do not use this book, it is empty mostly use Mehrieb instead Human Anatomy Books from Elsevier Healthhttp://www.us.elsevierhealth.com/Medicine/anatomy/ Atlas of Human Anatomy from Elsevier Health http://www.us.elsevierhealth.com/Netter/Netter-Basic-Science/book/9781416059516/Atlas-of-Human-Anatomy/ Pathology Books from Elsevier Health http://www.us.elsevierhealth.com/Medicine/Pathology/ Radiology Books from Elsevier Health http://www.us.elsevierhealth.com/Medicine/Radiology/
Connective tissue presentation Glands 2
Cartilage bone formation presentation Shoulder and superior appendage Bone pictures , diseases, x ray
7 Nervous system introduction, histology spinalcord reflexes presentation peripheral nervous system and somatic system
8 MUSCLE GENERALITY AND HISTOLOGY musclephysiology revised part1
9/ Endocrinology Endocrinology anatomy physiology Neuro endocrine a very basic conception not mine.
10/ Special Senses
All practical question are password protected now.For copyright reason and abuse, and also because some faculty cannot create their own question for exams MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY REVIEW QUESTION -MEGAN WHITE /SILVER KING MUSCL;ES GENERALITY REVIEW -MARSIA, MIRIAM,HEATHER, LAURA,ASHLEY NEUROLOGY REVIEW- LAURE, RACHEL,JENNY SMARTER THAN ME Jessica Long -Joselyn CoakleyMarsia Martin Neuroppt Jessica Long -Joselyn CoakleyMarsia Martin AlzheimesDieaseTheoretical approach Effects of Soy Isoflavones Erin M. Ballweber
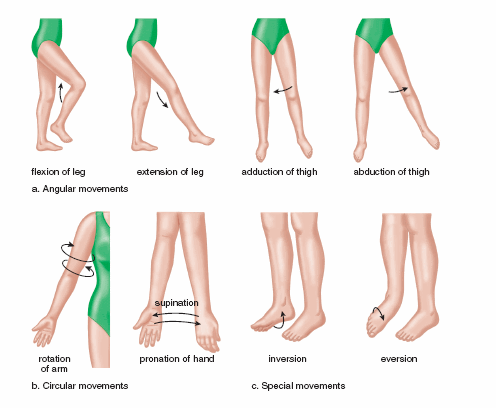
CCBC STUDENTS PRESENTATION: TISSUES:Kiah Cannon ,Eliana Langermann,Kyrie Pletts,R. Scott Murray Spinal Nerved: Kiah, scott, eliana, Jessica, kyrie Endocrinology: Kiah Cannon Jessica Hunt Eliana Langermann, Kyrie Pletts R. Scott Murray PERIOD 2 GENERAL REVIEW :Eugene , Justin, Caitriona, micah Kyrie PlettsR. Scott Murray Membrane transport : Megan White ,Silver King,Haeran Yu stem cells Xinxin Chang Generality introduction Telomeres Laurie Larsson stem cells, Lindsay A. Sarno Screening Children for Scoliosis-Lindsay Martin Multiple Sclerosis, the mysteries Disorder-Kamah C. David Osteoporosis: It’s Not Just for Women Anymore-Laurie Larsson stem cells-Rachel Lyons School Nurse Check for scoliosis-Otubu Osteogenic imperfecta -Laure STEM CELLS AND INTERESTS (LEUKEMIA)WILLIAM D JONES LAB MANUAL Joint movements. a. Angular movements increase or decrease the angle between the bones of a joint. b. Circular movements describe a circle or part of a circle. c. Special movements are unique to certain joints.[Mader: Understanding Human Anatomy & Physiology, Fifth Edition-The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2004] Hormone
Response
Adipose
epinephrine;
increase in triglyceride hydrolysis
Liver
epinephrine; increase in conversion of glycogen
Follicle FSH; LH increase in synthesis of estrogen, progesterone Adrenal cortex ACTH increase in synthesis of aldosterone, cortisol Cardiac muscle epinephrine increase in contraction rate Thyroid TSH secretion of thyroxin Bone cells
Parathyroid
increase in resorption of calcium
Skeletal muscle epinephrine conversion of glycogen to glucose Intestine epinephrine fluid secretion Kidney vasopressin resorption of water Blood platelets prostaglandin I inhibition of aggregation and secretion |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Rituals in the temples of Aesculapius included belief in the healing power of snakes. The god was said to hold a staff, around which his healing serpent was wound; from this, we get the modern symbol of medicine, the caduceus. Vesalius was the fifth generation of a line of doctors. He grew up close to an area called Gallows Hill, where criminals were executed and left to rot. As a child, he would look at bodily structures and take bones apart; he became interested in living anatomy. By age 10 or 11, Vesalius was taking animals to dissect. He focused not just on the structure of the body but on how the muscles and, possibly,digestion worked.
Professor Gunther von Hagens is the notorious anatomist who hasbecome a multimillionaire by pioneering a technique for preserving human bodies and then showing off his handiwork at gory public exhibitions across the globe Timeline c. 460 B.C. ....................................... Hippocrates born (d. 370 B.C.). c. 130 .............................................. Galen born (d. c. 200). 1514 ................................................ Andreas Vesalius born (d. 1564). 1543 ................................................ Vesalius publishes On the Workings of the Human Body (De Humani Corporis Fabrica). 1578 ................................................ William Harvey born (d. 1657). 1628 ................................................ Harvey publishes On the Movement of the Heart and Blood in Animals (De Motu Cordis). 1679 ................................................ Theophilus Bonetus of Geneva publishes A Repository of Anatomy Practiced on Corpses. 1682 ................................................ Giovanni Morgagni born (d. 1771). 1722 ................................................ Leopold Auenbrugger born (d. 1809). 1728 ................................................ John Hunter born (d. 1793). 1761 ................................................ Morgagni publishes On the Seats and Causes of Disease as Indicated by Anatomy De Sedibus). 1772 ................................................ Joseph Priestley discovers nitrous oxide. 1781 ................................................ René Laennec born (d. 1826). 1786 ................................................ Hunter publishes A Treatise on Venereal Disease. 1794 ................................................ Hunter publishes A Treatise on the Blood, Inflammation, and Gunshot Wounds. 1799 ................................................ Humphrey Davy discovers the anesthetic properties of nitrous oxide. 1805 ................................................ Charles Jackson is born (d. 1880). 1808 ................................................ Jean-Nicolas Corvisart rediscovers Auenbrugger’s technique of percussion. 1815 ................................................ Horace Wells is born (d. 1848); Crawford Long is born (d. 1878). 1816 ................................................ Laennec invents a prototype stethoscope. 1819 ................................................ Laennec publishes On Mediate Auscultation; William Morton is born (d. 1868). 1820 ................................................ Rudolf Virchow is born (d. 1902). 1822 ................................................ Louis Pasteur is born (d. 1895). 1827 ................................................ Joseph Lister is born (d. 1912). 1842 ................................................ Crawford Long uses ether as a surgical anesthetic (not publicized). 1844 ................................................ Gardiner Quincy Colton demonstrates laughing gas to Horace Wells. 1846 ................................................ William Morton publicly demonstrates ether used as an anesthesia. 1847 ................................................ James Simpson introduces chloroform as an anesthesia; Lister begins correspondence with Louis Pasteur. 1852 ................................................ William Halsted is born (d. 1922). 1858 ................................................ Virchow publishes Cellular Pathology. 1865 ................................................ Lister’s first clinical experiment with antisepsis. 1882 ................................................ Pasteur develops rabies vaccine. 1890 ................................................ Halsted introduces the use of rubber gloves in surgery. 1893 ................................................ Johns Hopkins Medical School opens; Halsted becomes its first professor of surgery. 1895 ................................................ W. C. Roentgen discovers x-rays. 1898 ................................................ Helen Taussig is born (d. 1986). 1910 ................................................ Vivien Thomas is born (d. 1985). 1944 ................................................ Taussig, Blalock, and Thomas develop surgery for blue babies. Doctors: The History of Scientific Medicine Revealed Through Biography Professor Sherwin B. Nuland, M.D., FACS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Danil Hammoudi.MD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||