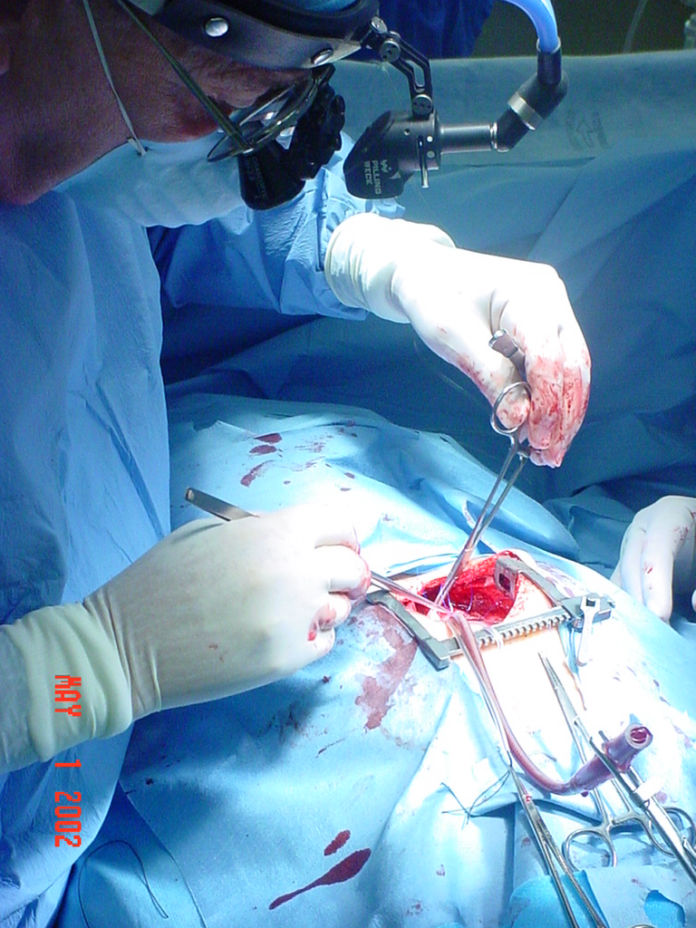
Services
Consulting
If you have a medical question, please feel free to ask. The important points are the following: you have medical questions we can answer, and you can do a little more to improve your health.
You are facing medical problems; you have a hard time to understand; we can assist you to discover a solution and understand.
You are currently suffering from some unknown symptoms and would like to know if they could be symptoms of a medical condition.
And while you're here, you also want to know another medical opinion about the best way of treatment for your medical condition
As we advise you, please be informed, but we cannot treat you.
-
This means you no longer need to go to a medical clinic in order to obtain a professional medical advice! When you make an appointment to see your doctor, it is critical that you are better informed about your medical condition.
Only 20% of the time after a doctor visit, patients still have questions, which suggests the other 80% of the time, they have additional questions.
We answer an average of 100 questions per month, and the number is increasing
So now you have a fantastic opportunity to consult with a doctor and get a medical advice, all from the comfort of your own home.
If you have any health concerns, you can speak with our medical advisors, and you will be happy with our medical consulting service.
Your question will be answered within the hour to 72 hours at the earliest, barring unforeseen circumstances.
Your questions are confidential, they are not shared, and they are not published unless you grant permission.
We will set up a time to call you and talk about your condition and possible solutions.